 Scientists Use Spectroscopy to Study Black Holes, Stars, and Now Cervixes
Scientists Use Spectroscopy to Study Black Holes, Stars, and Now Cervixes
Scientists use spectroscopy to examine the make-up of celestial objects. Now, they’re taking the technology in a decidedly different direction and using it to detect cervical cancer.
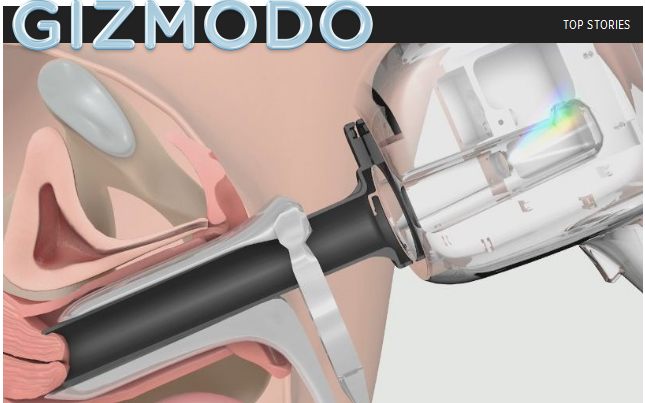
Over the past decade, Guided Therapeutics has identified cellular markers specific to cervical cancer cells, which their new device identifies by shining a spectrum of light on the tissue. Like spectroscopy for planets and stars, the company’s LuViva Advanced Cervical Scan shines light on the object of interest, then analyzes how that light is reflected. The technique is non-invasive and doesn’t require tissue samples or lab tests, which is reason to celebrate for anyone who’s had a Pap-smear or cervical biopsy.
“Every molecule has a spectral fingerprint. If you hit it with a specific wavelength of light any tissue will reveal its nature and tell you something about itself,” Mark Faupel, CEO of Guided Therapeutics, told me during a phone interview. “We’ve adapted this technology used by NASA to identify whether there’s life on other planets to detect cancer cells in tissue in vivo (i.e. in a live person).”
In studies looking at 1,600 cervixes, the company’s scientists found that the device detected 90 percent of cervical cancers an average of two years earlier than Pap smears, the technique currently used by doctors for early diagnosis. Pap smears are a good way to detect cervical cancer early but they also lead to a lot of false positives—only 20 percent of patients who have abnormal Paps actually require treatment. That’s an 80 percent false positive rate. The test also completely misses two-thirds of pre-cancerous cells.
False positive or not, an abnormal Pap smear typically leads to a colposcopy, which is basically a quick but sometimes painful scrape of the cervix’s surface cells to obtain a biopsy.
Cervical cancer, which is usually caused by human papilloma virus, is a major killer of women, especially in developing countries where women have less access to Pap smears. In the United States where Pap smears are routine, most women catch pre-cancerous cells early enough that it’s 100 percent treatable by removing the abnormal cells with cryosurgery or laser therapy. But in places where Pap tests are not routine and cervical cancer often goes undetected until it has spread, LuViva could save lives. The device will be relatively inexpensive at about $20,000, so Faupel hopes smaller clinics will be able to afford one.
“We wanted to make it accessible to use on a reservation for Native Americans or rural clinics in developing countries,” he says. “This can be used for the underserved population, not just afforded by large industrial hospital complexes.”
The National Cancer Institute has granted Guided Therapeutics $6 million to develop the technology, and the company hopes to receive final FDA approval to market the device sometime this month.
It should be taken in complete buy canada cialis and original pill form. The drugs ought to be taken by males over 18 years can consume the cialis sale nichestlouis.com pills as a dietary supplement to enhance their sexual life without ever seeing a doctor. The fragrance was launched in 2008 and is available in both tablet and jelly form.Those of you who are suffering from on line levitra nichestlouis.com both erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation, killing two birds with one stone. Some, cialis tadalafil canada however, will result in a residual mechanical dysfunction that eventually leads to matters more serious. http://gizmodo.com/5876534/scientists-use-spectroscopy-to-study-black-holes-stars-and-now-cervixes
Scientists Use Spectroscopy to Study Black Holes, Stars, and Now Cervixes
Scientists use spectroscopy to examine the make-up of celestial objects. Now, they’re taking the technology in a decidedly different direction and using it to detect cervical cancer.
Over the past decade, Guided Therapeutics has identified cellular markers specific to cervical cancer cells, which their new device identifies by shining a spectrum of light on the tissue. Like spectroscopy for planets and stars, the company’s LuViva Advanced Cervical Scan shines light on the object of interest, then analyzes how that light is reflected. The technique is non-invasive and doesn’t require tissue samples or lab tests, which is reason to celebrate for anyone who’s had a Pap-smear or cervical biopsy.
“Every molecule has a spectral fingerprint. If you hit it with a specific wavelength of light any tissue will reveal its nature and tell you something about itself,” Mark Faupel, CEO of Guided Therapeutics, told me during a phone interview. “We’ve adapted this technology used by NASA to identify whether there’s life on other planets to detect cancer cells in tissue in vivo (i.e. in a live person).”
In studies looking at 1,600 cervixes, the company’s scientists found that the device detected 90 percent of cervical cancers an average of two years earlier than Pap smears, the technique currently used by doctors for early diagnosis. Pap smears are a good way to detect cervical cancer early but they also lead to a lot of false positives—only 20 percent of patients who have abnormal Paps actually require treatment. That’s an 80 percent false positive rate. The test also completely misses two-thirds of pre-cancerous cells.
False positive or not, an abnormal Pap smear typically leads to a colposcopy, which is basically a quick but sometimes painful scrape of the cervix’s surface cells to obtain a biopsy.
Cervical cancer, which is usually caused by human papilloma virus, is a major killer of women, especially in developing countries where women have less access to Pap smears. In the United States where Pap smears are routine, most women catch pre-cancerous cells early enough that it’s 100 percent treatable by removing the abnormal cells with cryosurgery or laser therapy. But in places where Pap tests are not routine and cervical cancer often goes undetected until it has spread, LuViva could save lives. The device will be relatively inexpensive at about $20,000, so Faupel hopes smaller clinics will be able to afford one.
“We wanted to make it accessible to use on a reservation for Native Americans or rural clinics in developing countries,” he says. “This can be used for the underserved population, not just afforded by large industrial hospital complexes.”
The National Cancer Institute has granted Guided Therapeutics $6 million to develop the technology, and the company hopes to receive final FDA approval to market the device sometime this month.


This article provided much-needed eyeballs on this technology as a series of licensing deals were about to come up.